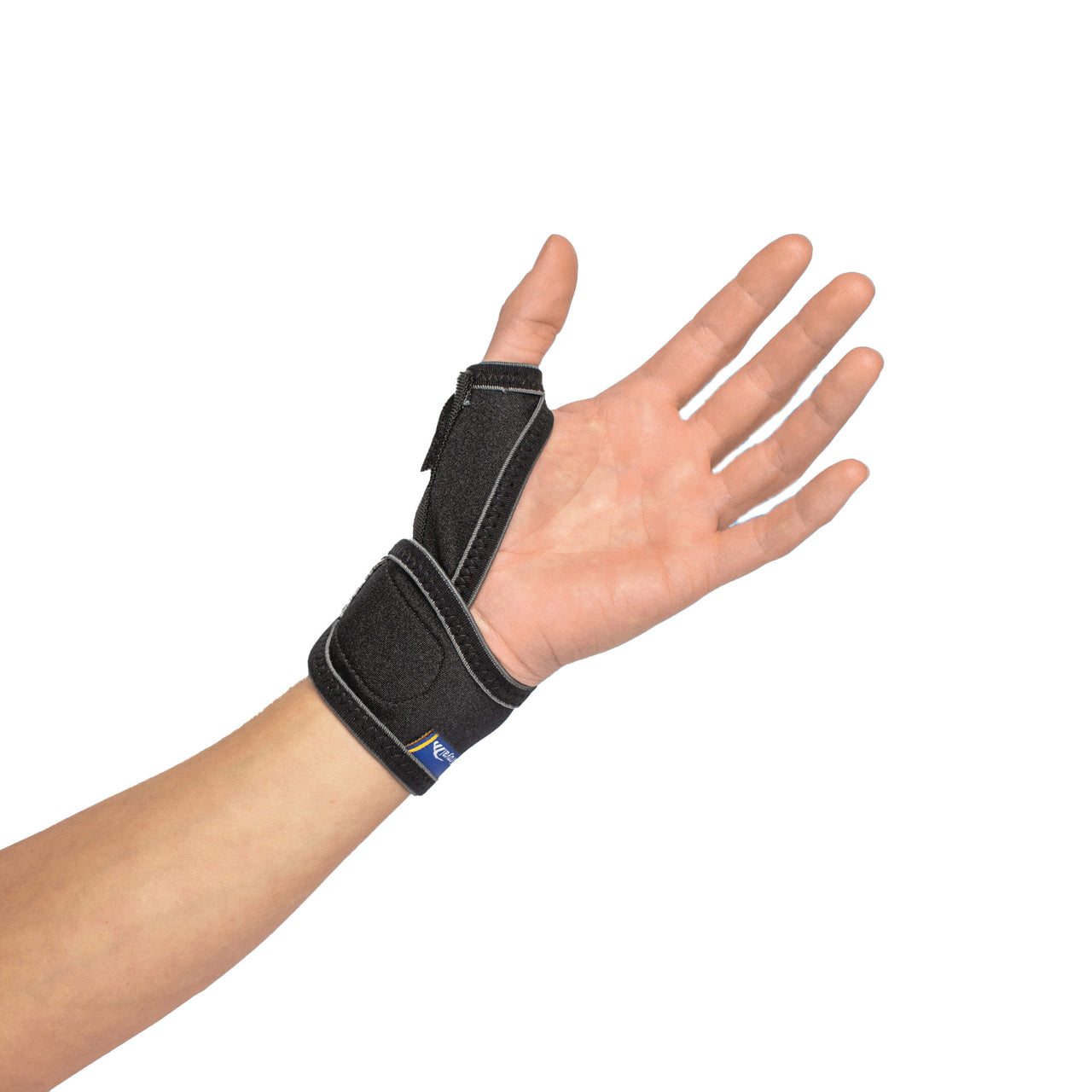
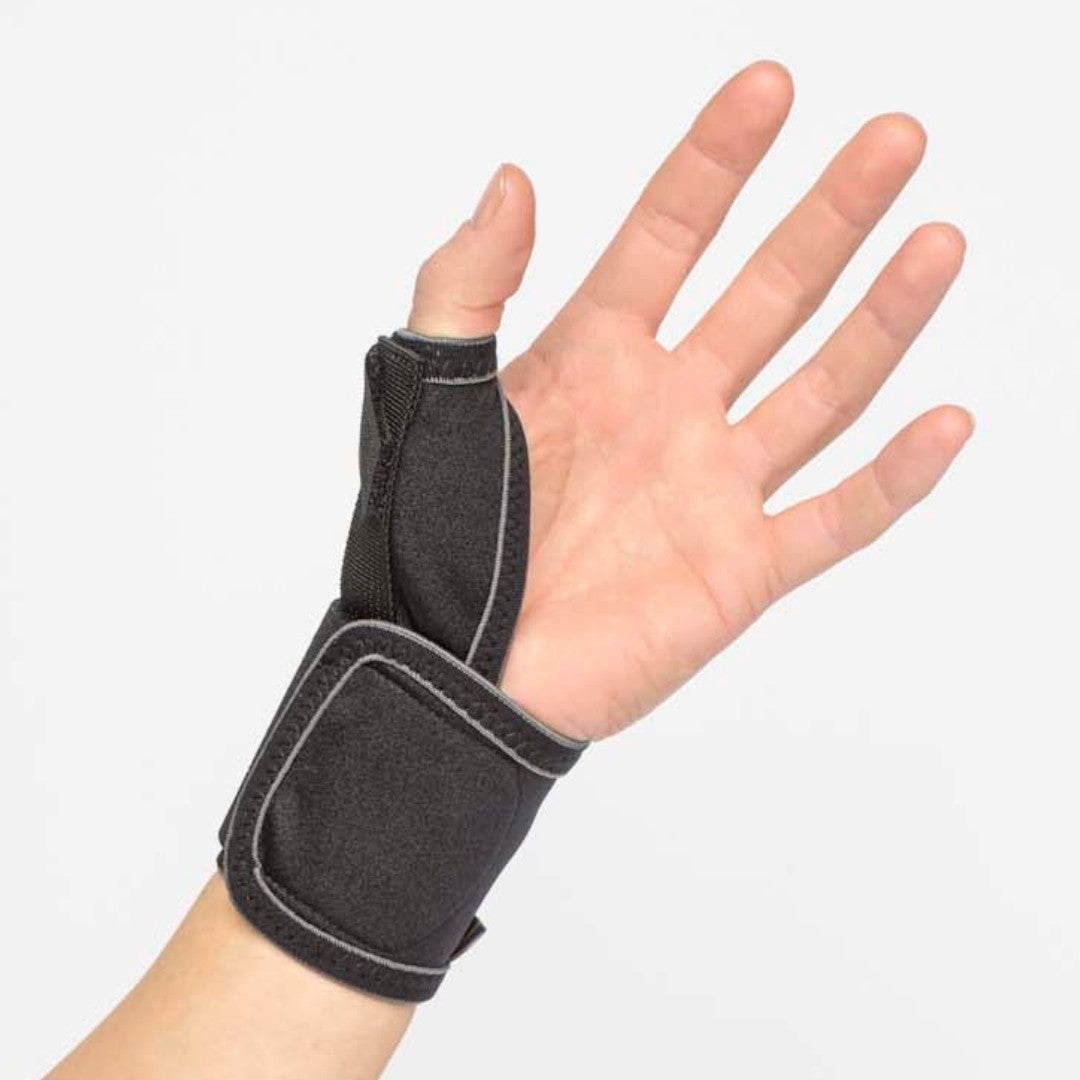
Thumb osteoarthritis, also known as thumb osteoarthritis or joint failure, is a condition in which the cartilage in the thumb's base joint breaks down. This leads to pain, stiffness, and decreased strength, making simple everyday tasks like opening a can or holding a milk carton more difficult.
What is osteoarthritis of the thumb?
In osteoarthritis of the thumb, the articular cartilage that normally acts as a sliding surface in the joint deteriorates. The cartilage allows the thumb to move smoothly and without pain. When the cartilage wears down, mobility decreases and the joint becomes more stressed, causing pain and stiffness. Osteoarthritis most often affects the thumb's base joint, the CMC joint, which is located at the base of the thumb near the wrist.
Common causes & risk factors
Osteoarthritis of the thumb often develops gradually and becomes more common with age. The wear and tear of the articular cartilage occurs naturally, but the risk increases if the thumb is subjected to one-sided or heavy work that puts stress on the joint. Repetitive movements in the thumb-index finger grip are also a contributing factor, as is heredity for osteoarthritis. Age itself is a risk factor because the cartilage gradually weakens over time.
Symptom
- Numbness, local pain in the thumb, often at the base of the thumb
- Pain with strain, especially when gripping or twisting movements
- Reduced grip strength, especially in the thumb-index finger grip
- Stiffness and swelling in the base of the thumb
-
In more extensive osteoarthritis, pain even at rest
When should you seek medical attention?
Seek medical attention if the pain becomes persistent and affects everyday life, if you lose a lot of strength in your hand, or if the swelling increases.
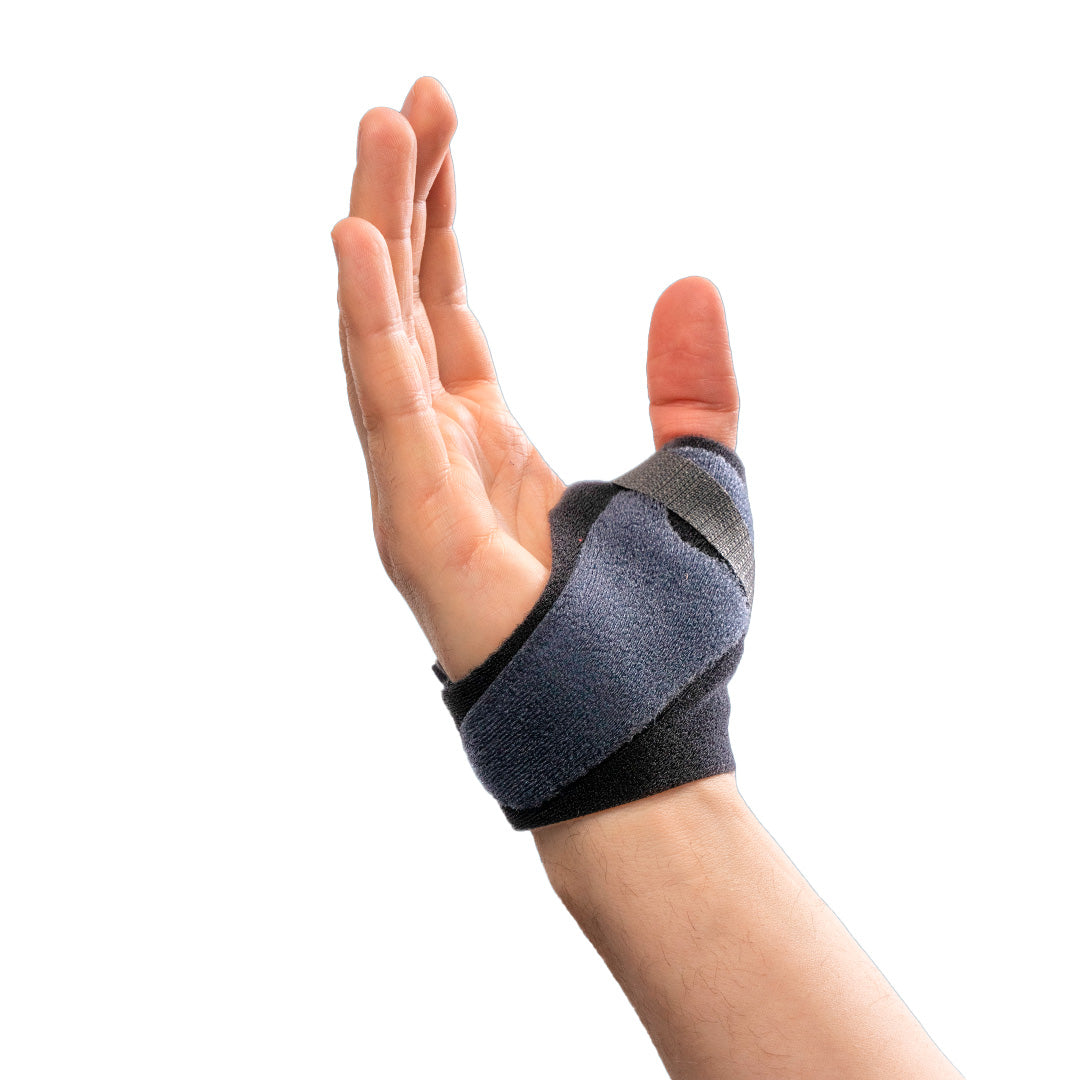
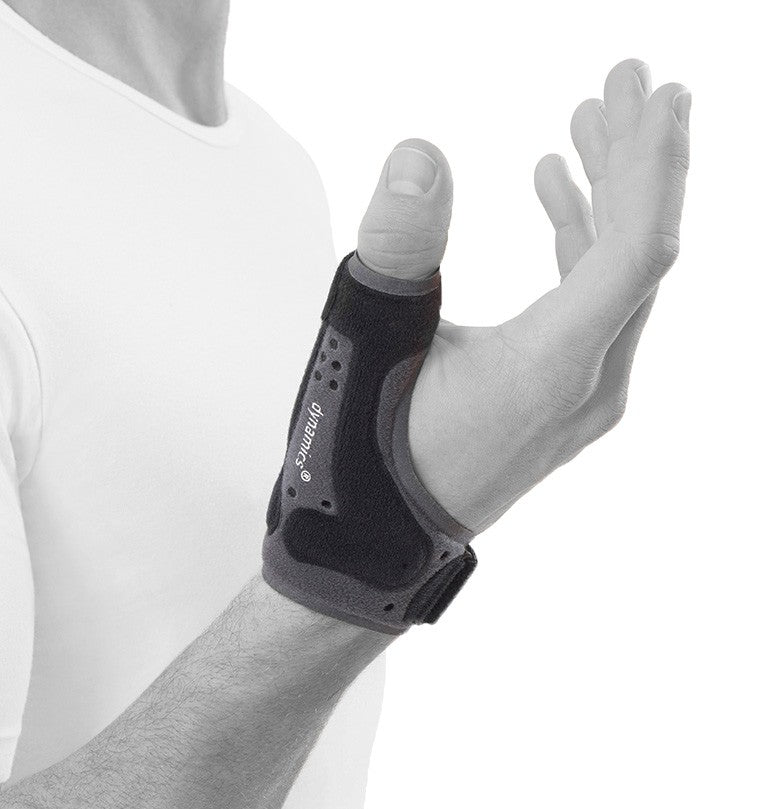
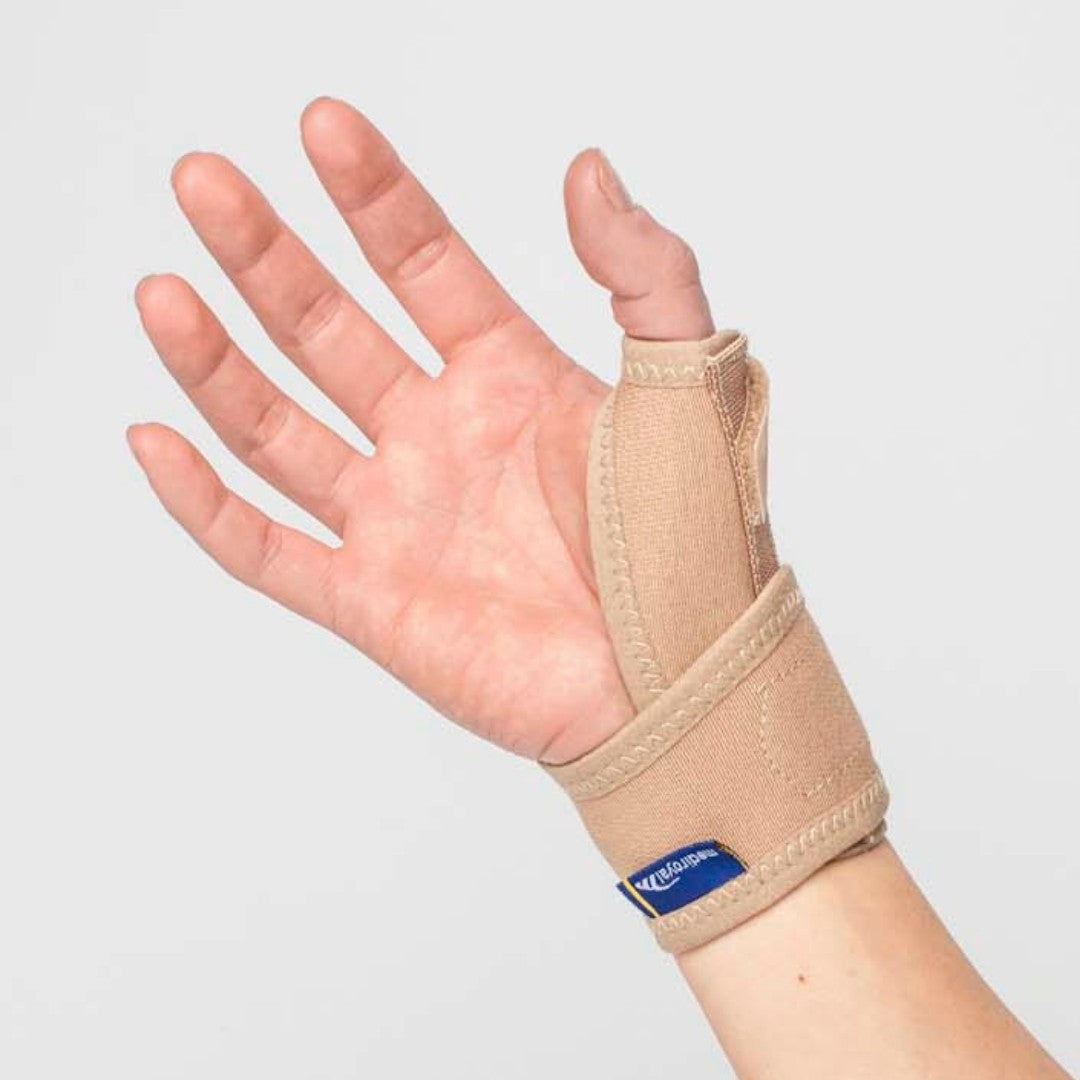
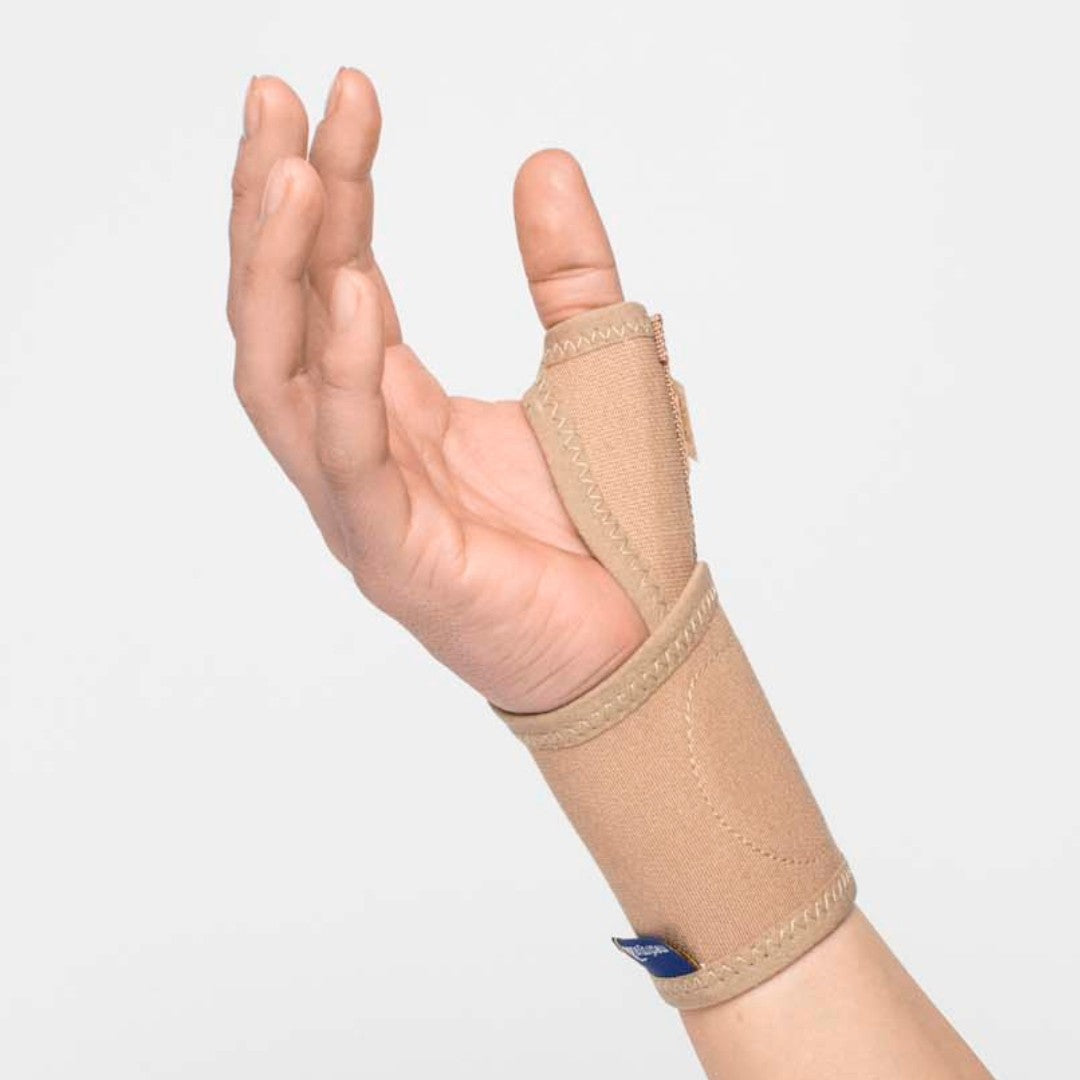
Recommended protection & support
To alleviate the discomfort of thumb osteoarthritis, various supports and aids can be used. Stabilizing thumb supports relieve the pressure on the thumb's base joint and provide increased stability, while relieving thumb supports can reduce pain and swelling during activity. Ergonomic aids that facilitate grip and reduce strain in everyday life can also make a big difference in preserving function and reducing discomfort.